Non-destructive testing (NDT) types are essential in the manufacturing industry for pumps and industrial valves to ensure the quality and integrity of components without causing damage. These techniques allow manufacturers to detect defects and assess material properties effectively, maintaining high safety and efficiency standards. In this article, we will explore in detail the most commonly used methods in non-destructive testing, highlighting their specific applications and advantages.
Main Methods of Non-Destructive Testing
Visual Inspection (VT)
The most straightforward method, visual inspection, involves a thorough examination of a component’s surface. Tools such as flashlights, magnifying glasses, and visual amplification equipment are used to detect surface defects (e.g., cracks, corrosion, and misalignments). This method is often the first step in an evaluation process, as it allows for the detection of obvious problems without complex equipment.
- Advantages:
- Simple and quick to implement.
- Does not require sophisticated equipment or prior preparation.
- Applications:
- Preliminary inspection and quality control of large parts.
- Evaluation of welds and surface finishes.
In particular, visual inspection is crucial for detecting defects in essential components like centrifugal pumps, ensuring their proper functioning and extending their lifespan.
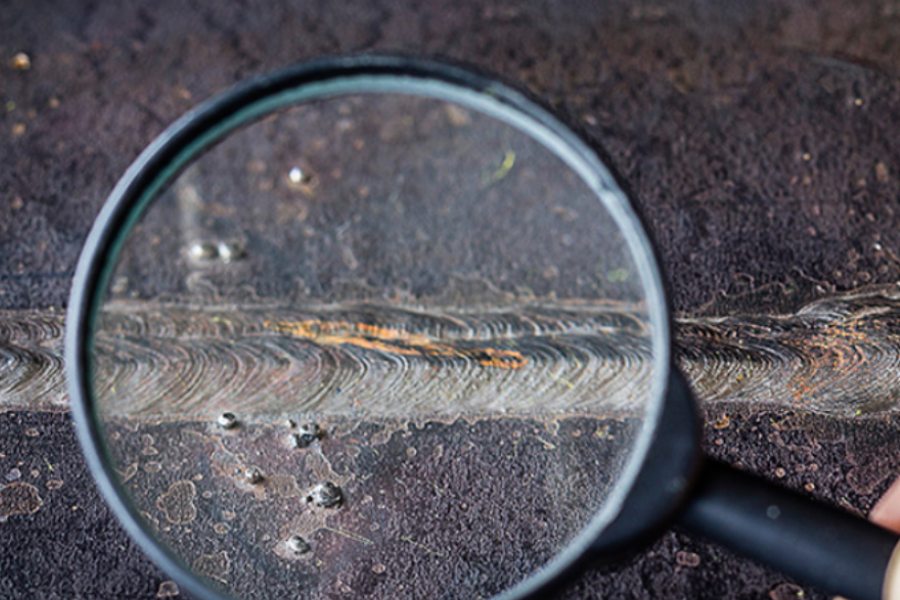

Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)
This method, highly sensitive to surface discontinuities in non-porous materials, begins with careful cleaning of the study object to remove residues that could hide defects. A penetrant liquid is applied to the clean surface and allowed to infiltrate open cracks. Subsequently, a developer is sprayed onto the surface, absorbing the liquid from the cracks and showing a clear image of any defects.
- Advantages:
- High sensitivity for detecting surface defects.
- Relatively inexpensive and easy to apply.
- Applications:
- Inspection of welds and critical components.
- Detection of surface cracks and porosities in valves and pumps.
The use of liquid penetrants is especially useful in inspecting materials like metals and ceramics, where detecting surface cracks is crucial to ensuring the component’s structural integrity. This technique is widely adopted in the industry due to its ease of use and low cost compared to other methods.

Magnetic Particle Inspection (MT)
Used exclusively on ferromagnetic metals, this technique employs an external magnetic field to magnetize the component. After magnetizing the element, fine magnetic particles are spread over the surface. These particles gather in areas of magnetic discontinuities caused by defects, visible under conventional or ultraviolet light.
- Advantages:
- Capable of detecting both surface and subsurface defects.
- Quick and efficient process.
- Applications:
- Evaluation of pump and valve components where detecting internal cracks is crucial.
- Inspection of pump shafts and housings.
The magnetic particle method is highly effective in detecting cracks not visible on the surface, providing a deeper insight into the material’s integrity. Additionally, it is a fast method, making it ideal for routine inspections and preventive maintenance.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
This method uses high-frequency sound waves transmitted through the component. The ultrasound reflects at interfaces, such as material boundaries or internal defects, returning to the transducer. These data are analyzed to calculate the location and size of the detected defects, providing a detailed view of the material’s internal integrity.
- Advantages:
- High precision in detecting internal defects.
- Can be used on a wide variety of materials and shapes.
- Applications:
- Inspection of pump housings and internal components.
- Evaluation of welds in critical areas.
Ultrasonic technology allows not only the detection of internal defects but also the precise measurement of material thickness, which is essential in assessing wear and corrosion. This method is particularly valuable in inspecting critical components where safety is a priority.

Industrial Radiography (RT)
Similar to medical radiography but adapted for industrial materials, this technique uses X-rays or gamma rays to penetrate materials and capture images of their internal structure. These images reveal hidden defects such as internal corrosion, cracks, and porosities that would otherwise be invisible.
- Advantages:
- Provides a detailed inspection of the internal structure.
- Ideal for complex and high-precision components.
- Applications:
- Evaluation of welds and internal structures in valves and pumps.
- Inspection of castings and critical components.
Industrial radiography is an advanced technique that offers a clear view of the material’s internal structure, allowing inspectors to identify hidden defects that could compromise the component’s integrity. However, it requires specialized equipment and trained personnel to handle the radiation safely.
Technological Advances in NDT Techniques
Modern trends in NDT involve the digitization and automation of traditional processes. For example, industrial radiography has evolved with the development of digital radiography, which provides clearer and more precise images and significantly reduces radiation exposure time. In ultrasonics, advanced techniques such as phased array ultrasonics allow for faster and more accurate examination of complex components. Magnetic particle inspection benefits from equipment that automates the application and collection of particles, improving the reproducibility of tests.
Combining non-destructive testing methods with measurement instruments, such as the measuring arm and high-precision procedures used in our Metrology Room, ensures that each component not only meets quality standards but also optimizes its performance and durability in critical applications.
Specific Applications of Non-Destructive Testing in Various Industries
In ships and submarines, NDT is crucial for detecting metal fatigue and corrosion under insulation, critical for safety in water. Additionally, inspecting flow control valves in the naval industry is vital to ensure these components function correctly under demanding conditions, preventing potential failures in critical systems.
These industries require rigorous inspection of pipes, tanks, and structures subject to extreme and corrosive conditions. Advanced ultrasonic techniques and digital radiography are widely used for the early detection of material deterioration.
In applications where materials are exposed to extremely low temperatures, NDT ensures the structural integrity of containers and pipes handling liquefied gases. Precise and meticulous inspection is essential to ensure the safe and efficient operation of cryogenic pumps, which operate under extreme temperature and pressure conditions.
The growing dependence on desalination involves extensive use of NDT to prevent corrosion and erosion in pipes and membranes exposed to saline water.
This industry requires constant monitoring of boilers and pipes to prevent blockages and corrosion, using techniques such as radiography and ultrasonics.
Here, NDT allows the detection of failures in treatment plant structures and conduits, crucial to preventing leaks and contamination.
Asimer Group’s Expertise in Non-Destructive Testing
For over a decade and a half, Asimer Group has developed extensive experience in applying non-destructive testing (NDT). The increasing demand and stringent specifications of the industrial pump and valve industries have driven us to continuously perfect our NDT techniques, motivated primarily by two reasons:
- Non-Destructive Testing in Machined Cast Parts
A significant proportion of our machined parts come from foundries. These cast parts are prone to surface quality issues that can be effectively identified and mitigated using NDT before final machining according to design specifications.
At Asimer Group, we have Level II certified technicians in various NDT modalities, allowing us to offer these specialized services directly to our customers, including Liquid Penetrant Testing (LPT) and Visual Inspection (VT). Additionally, our ability to ensure accuracy in CNC machining guarantees that each component meets the highest quality and performance standards.
- Non-Destructive Testing in Welded or Overlay Components
Another important segment of our supply includes parts with welded joints or overlay treatments. For example, welds that join rings to valve bodies, such as gate, globe, or check valves, are meticulously inspected using LPI to confirm the optimal quality of these connections. Additionally, critical components such as axial flow check valves are inspected to ensure their integrity and functionality in demanding applications.
Regarding the use of overlays, Asimer Group has executed numerous projects, particularly with carbon steel coated with Inconel 625. These projects invariably require compliance with specific NDT criteria.
Visual Inspection and Liquid Penetrant Testing techniques are essential to verify that the overlay-treated surface meets the quality standards required for each project. Moreover, we use advanced methods such as TIG welding in our operations, ensuring a high-precision and durable finish.
The competence and rigor in our NDT processes allow us to ensure that all parts, whether cast or welded, meet the highest quality standards demanded by our customers and the industry in general.
Conclusion
The incorporation of advanced technology in NDT methods has greatly expanded their capabilities, allowing industries to maintain safety and reliability while advancing towards process optimization and greater environmental sustainability. These methods continue to evolve to meet the challenges of an increasingly complex and demanding industrial landscape, ensuring that materials and working components meet or exceed quality and performance expectations.
Non-destructive testing, with its ability to inspect without causing damage, is more than ever a critical component of modern engineering, playing a decisive role in prolonging the lifespan of components and ensuring the safety of operations in numerous industrial sectors. With each technological advance, these techniques become even more powerful tools for engineers and technicians worldwide.


